



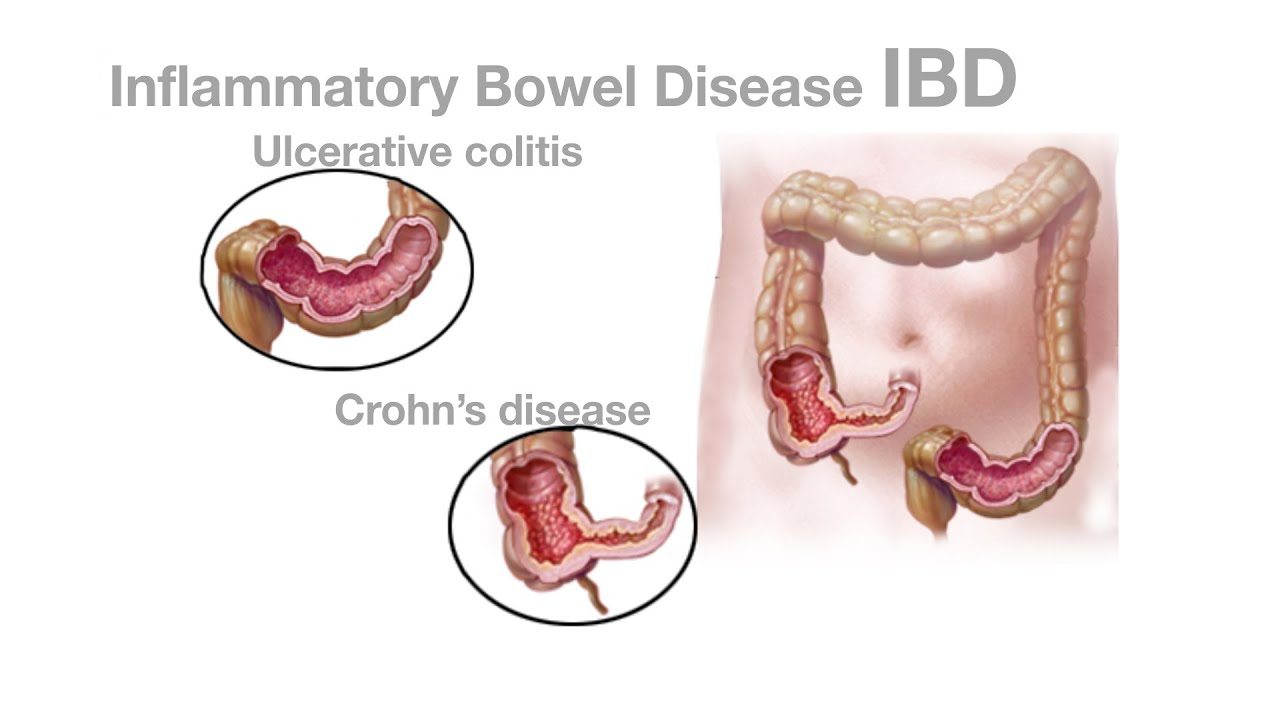
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is a chronic condition that involves inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. The two main types of IBD are Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. While the exact cause of IBD is not fully understood, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. Here is some information about IBD:
Our team of highly skilled surgical gastroenterologists combines advanced
surgical
techniques
with extensive
knowledge of the gastrointestinal system
to offer comprehensive
treatment
options. Whether you're seeking consultation for a specific condition or in need of surgical
intervention, we are dedicated to providing personalized care and improving your digestive
health.
We understand the importance of comprehensive and personalized care. We believe in establishing strong doctor-patient relationships built on trust.
Old Airport Road, Bangalore
+91 8968412271
© AppAddIndia. All Rights Reserved.